템플릿
함수나 클래스를 개별적으로 다시 작성하지 않아도, 여러 자료형으로 사용할 수 있도록 만들어 놓은 틀이다.
함수 템플릿과 클래스 템플릿으로 나누어진다.
함수템플릿
–함수 템플릿은 template< >로 시작한다. < > 사이에 템플릿에서 사용할 임의의 타입 이름을 인자로 나열한다. 인자로 전달되는 타입 이름을 템플릿 타입 이름이라고 하며 식별자로서 마음대로 정할 수 있지만 일반적인 관례로 T, _Tx, _Ty, T1 등과 같이 가능하면 짧게 만든다.
–템플릿 타입 이름을 나타내기 위하여 typename이라는 키워드를 사용하는데 구형 컴파일러 는 typename 대신 class를 사용하였다. typename, class 모두 사용 가능하지만 가능하면 typename을 사용하는 편이 좋다.
template< > 다음에는 함수 정의와 똑같은 형식의 함수 틀이 오게 되는데, 함수 틀은 템플릿 타입 이름을 사용하여 함수를 정의한 것이다. 따라서 함수의 반환 타입이나 인자 타입, 함수 본 체에서 사용되는 모든 타입은 템플릿 타입 이름으로 대체할 수 있다.
함수 템플릿
|
template<typename T> T add(T a, T b) { return a + b; } |
|
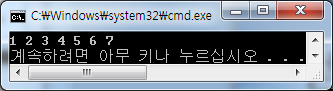
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<typename T> T add(T a, T b) { return a + b; } int main() { cout<< add<int>(1, 2) <<endl; cout<< add<double>(3.14, 5.0) <<endl; return 0; } |
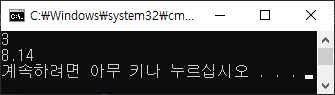
함수 템플릿의 구체화
|
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; } double add(double a, double b) { return a + b; } int main() { cout<< add(1, 2) <<endl; cout<< add(3.14, 5.0) <<endl; return 0; } |
|
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<typename T> T add(T a, T b) { cout << "T add(T a, T b)" <<endl; return a + b; } int add(int a, int b) { cout << "add(int a, int b)" <<endl; return a + b; } double add(double a, double b) { cout << "add(double a, double b)" <<endl; return a + b; } int main() { cout<< add(1, 2) <<endl; cout<< add(3.14, 5.0) <<endl; cout<< add<int>(1, 2) <<endl; cout<< add<double>(3.14, 5.0) <<endl; return 0; } |
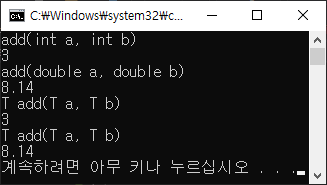 |
|
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<typename T1, typename T2> void ShowData(double num) { cout << (T1)num << ", " << (T2)num << endl; } int main() { ShowData<char, int>(65); ShowData<char, int>(67); ShowData<char, double>(68.9); ShowData<short, double>(69.2); ShowData<short, double>(70.4); return 0; }  |
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<typename T> T Max(T a, T b) { return a > b ? a : b; } int main() { cout << Max(11, 15) << endl; cout << Max('T', 'Q') << endl; cout << Max(3.5, 7.5) << endl; cout << Max("Simple", "Best") << endl; return 0; }  |
함수 템플릿의 특수화
|
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<typename T> T Max(T a, T b) { return a > b ? a : b; } template<> //특수화 표현 char* Max(char *a, char *b) { cout<<"char* Max<char*>(char *a, char *b)"<<endl; return strlen(a) > strlen(b)? a : b; } template<> const char* Max(const char *a, const char *b) { cout<<"const char* Max<const char*>(const char *a, const char *b)"<<endl; return strcmp(a, b) > 0 ? a : b; } int main() { cout << Max(11, 15) << endl; cout << Max('T', 'Q') << endl; cout << Max(3.5, 7.5) << endl; cout << Max("Simple", "Best") << endl; char str1[] = "Simple"; char str2[] = "Best"; cout<< Max(str1, str2) << endl; return 0; } |

클래스 템플릿
파일 : PointTemplate.h
|
#ifndef __POINT_TEMPLATE_H_ #define __POINT_TEMPLATE_H_ template<typename T> class Point { private: T xpos, ypos; public: Point(T x=0, T y=0); void ShowPosition() const; }; #endif |
파일 : PointTemplate.cpp
|
#include <iostream> #include "PointTemplate.h" using namespace std; template<typename T> Point<T>::Point(T x=0, T y=0):xpos(x), ypos(y) { } template<typename T> void Point<T>::ShowPosition() const { cout<<'['<<xpos<<", "<<ypos<<']'<<endl; } |
파일 : PointMain.cpp
|
int main() { Point<int> pos1(3, 4); pos1.ShowPosition(); Point<double> pos2(2.4, 3.6); pos2.ShowPosition(); Point<char> pos3('p', 'f'); pos3.ShowPosition(); return 0; } |

배열 클래스의 템플릿화
파일 : ArrayTemplate.h
|
#ifndef __ARRAY_TEMPLATE_H_ #define __ARRAY_TEMPLATE_H_ #include <iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; template <typename T> class BoundCheckArray { private: T *arr; int arrlen; BoundCheckArray(const BoundCheckArray& arr){} BoundCheckArray& operator=(const BoundCheckArray& arr){} public: BoundCheckArray(int len); T& operator[] (int idx); T operator[] (int idx) const; int GetArrLen() const; ~BoundCheckArray(); }; template <typename T> BoundCheckArray<T>::BoundCheckArray(int len):arrlen(len) { arr = new T[len]; } |
template <typename T> T& BoundCheckArray<T>::operator[](int idx) { if(idx < 0 || idx >= arrlen) { cout<<"Array index out of bound exception"<<endl; exit(1); } return arr[idx]; } template <typename T> T BoundCheckArray<T>::operator[] (int idx) const { if(idx < 0 || idx >= arrlen) { cout<<"Array index out of bound exception"<<endl; exit(1); } return arr[idx]; } template <typename T> int BoundCheckArray<T>::GetArrLen() const { return arrlen; } template <typename T> BoundCheckArray<T>::~BoundCheckArray() { delete []arr; } #endif |
|
파일 : Point.h #define __POINT_H_ #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Point { private: int xpos, ypos; public: Point(int x=0, int y=0); friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Point& pos); }; #endif #include <iostream> #include "Point.h" using namespace std; Point::Point(int x, int y):xpos(x), ypos(y) {} ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Point& pos) { os<<'['<<pos.xpos<<", "<<pos.ypos<<']'<<endl; return os; } 파일 : BoundArrayMain.cpp #include <iostream> #include "ArrayTemplate.h" #include "Point.h" using namespace std;
|
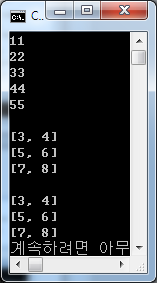
int main() { /* int형정수저장*/ BoundCheckArray<int> iarr(5); for(int i=0; i<5; i++) iarr[i] = (i+1)*11; for(int i=0; i<5; i++) cout<<iarr[i]<<endl; cout<<endl; /* Pint 객체저장*/ BoundCheckArray<Point> oarr(3); oarr[0]=Point(3, 4); oarr[1]=Point(5, 6); oarr[2]=Point(7, 8); for(int i=0; i<oarr.GetArrLen(); i++) cout<<oarr[i]; cout<<endl; /* Pint 객체의주소값저장*/ typedef Point *POINT_PTR; BoundCheckArray<POINT_PTR> parr(3); parr[0]=new Point(3, 4); parr[1]=new Point(5, 6); parr[2]=new Point(7, 8); for(int i=0; i<parr.GetArrLen(); i++) cout<<*(parr[i]);
delete parr[0]; delete parr[1]; delete parr[2]; return 0; } |
배열 클래스의 템플릿화2
파일 : ArrayTemplate.h
|
#ifndef __ARRAY_TEMPLATE_H_ #define __ARRAY_TEMPLATE_H_ #include <iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; template <typename T> class BoundCheckArray { private: T *arr; int arrlen; BoundCheckArray(const BoundCheckArray& arr){} BoundCheckArray& operator=(const BoundCheckArray& arr){} public: BoundCheckArray(int len); T& operator[] (int idx); T operator[] (int idx) const; int GetArrLen() const; ~BoundCheckArray(); }; template <typename T> BoundCheckArray<T>::BoundCheckArray(int len):arrlen(len) { arr = new T[len]; } template <typename T> T& BoundCheckArray<T>::operator[](int idx) { if(idx < 0 || idx >= arrlen) { cout<<"Array index out of bound exception"<<endl; exit(1); } return arr[idx]; } template <typename T> T BoundCheckArray<T>::operator[] (int idx) const { if(idx < 0 || idx >= arrlen) { cout<<"Array index out of bound exception"<<endl; exit(1); } return arr[idx]; } template <typename T> int BoundCheckArray<T>::GetArrLen() const { return arrlen; } template <typename T> BoundCheckArray<T>::~BoundCheckArray() { delete []arr; } #endif |
파일 : PointTemplate.h
|
#ifndef __POINT_TEMPLATE_H_ #define __POINT_TEMPLATE_H_ template <typename T> class Point { private: T xpos, ypos; public: Point(T x=0, T y=0); void ShowPosition() const; }; template <typename T> Point<T>::Point(T x=0, T y=0):xpos(x), ypos(y) {} template <typename T> void Point<T>::ShowPosition() const { cout<<'['<<xpos<<", "<<ypos<<']'<<endl; } #endif |
파일 : BoundArrayMain.cpp
|
#include <iostream> #include "ArrayTemplate.h" #include "PointTemplate.h" using namespace std; int main() { BoundCheckArray<Point<int>> oarr(3); oarr[0]=Point<int>(3, 4); oarr[1]=Point<int>(5, 6); oarr[2]=Point<int>(7, 8); for(int i=0; i<oarr.GetArrLen(); i++) oarr[i].ShowPosition(); cout<<endl; BoundCheckArray<Point<double>> oarr2(3); oarr2[0]=Point<double>(3.14, 4.31); oarr2[1]=Point<double>(5.09, 6.07); oarr2[2]=Point<double>(7.82, 8.54); for(int i=0; i<oarr2.GetArrLen(); i++) oarr2[i].ShowPosition(); cout<<endl; typedef Point<int> *POINT_PTR; BoundCheckArray<POINT_PTR> parr(3); parr[0]=new Point<int>(11, 12); parr[1]=new Point<int>(13, 14); parr[2]=new Point<int>(15, 16); for(int i=0; i<parr.GetArrLen(); i++) parr[i]->ShowPosition();
delete parr[0]; delete parr[1]; delete parr[2]; return 0; } |

특정 템플릿 클래스의 객체를 인자로 받는 일반함수의 정의와 friend 선언
|
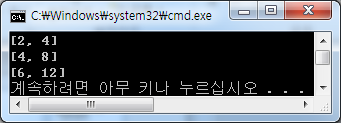
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T> class Point { private: T xpos, ypos; public: Point(T x=0, T y=0); void ShowPosition() const; friend Point<int> operator+(const Point<int>&, const Point<int>&); friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Point<int>& pos); }; template <typename T> Point<T>::Point(T x=0, T y=0):xpos(x), ypos(y) {} template <typename T> void Point<T>::ShowPosition() const { cout<<'['<<xpos<<", "<<ypos<<']'<<endl; } Point<int> operator+(const Point<int>& pos1, const Point<int>& pos2) { return Point<int>(pos1.xpos+pos2.xpos, pos1.ypos+pos2.ypos); } ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Point<int>& pos) { os<<'['<<pos.xpos<<", "<<pos.ypos<<']'<<endl; return os; } int main() { Point<int> pos1(2, 4); Point<int> pos2(4, 8); Point<int> pos3=pos1+pos2; cout<<pos1<<pos2<<pos3; return 0; } |
클래스 템플릿의 특수화
|
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std; template <typename T> class Point { private: T xpos, ypos; public: Point(T x=0, T y=0): xpos(x), ypos(y) {} void ShowPosition() const { cout<<'['<<xpos<<", "<<ypos<<']'<<endl; } }; template <typename T> class SimpleDataWrapper { private: T mdata; public: SimpleDataWrapper(T data):mdata(data) {} void ShowDataInof() { cout<<"Data : "<<mdata<<endl; } }; template <> class SimpleDataWrapper <char*> { private: char* mdata; public: SimpleDataWrapper(char* data) { mdata=new char[strlen(data)+1]; strcpy(mdata, data); } void ShowDataInof() { cout<<"String : "<<mdata<<endl; cout<<"Length : "<<strlen(mdata)<<endl; } SimpleDataWrapper() { delete []mdata; } }; template <> class SimpleDataWrapper <Point<int>> { private: Point<int> mdata; public: SimpleDataWrapper(int x, int y):mdata(x, y) {} void ShowDataInof() { mdata.ShowPosition(); } }; int main() { SimpleDataWrapper<int> iwrap(170); iwrap.ShowDataInof(); SimpleDataWrapper<char*> swrap("class Template Specialization"); swrap.ShowDataInof(); SimpleDataWrapper<Point<int>> poswrap(3, 7); poswrap.ShowDataInof(); return 0; } |

클래스 템플릿의 부분 특수화
|
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T1, typename T2> class MySimple { public: void WhoAreYou() { cout<<"size of T1 "<<sizeof(T1)<<endl; cout<<"size of T2 "<<sizeof(T2)<<endl; cout<<"<typename T1, typename T2>"<<endl; } }; template <> class MySimple<int, double> { public: void WhoAreYou() { cout<<"size of int "<<sizeof(int)<<endl; cout<<"size of double "<<sizeof(double)<<endl; cout<<"<int, double>"<<endl; } }; /* template <typename T1> class MySimple<T1, double> //T2를double로부분특수화 { public: void WhoAreYou() { cout<<"size of T1 "<<sizeof(T1)<<endl; cout<<"size of double "<<sizeof(double)<<endl; cout<<"<T1, double>"<<endl; } }; */ int main() { MySimple<char, double> obj1; obj1.WhoAreYou(); cout<<endl; MySimple<int, long> obj2; obj2.WhoAreYou(); cout<<endl; MySimple<int, double> obj3; obj3.WhoAreYou(); return 0; } |
부분특수화 주석처리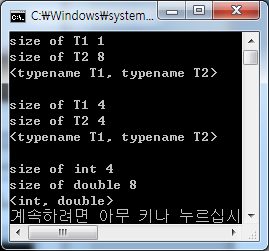 |
부분특수화 주석해제 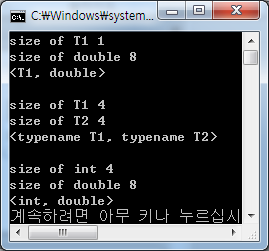 |
템플릿 인자(템플릿 매개변수에 변수를 선언)
|
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T, int len> class SimpleArray { private: T arr[len]; public: T& operator[] (int idx) { return arr[idx]; } SimpleArray<T, len>& operator=(const SimpleArray<T, len>& ref) { for(int i=0; i<len; i++) arr[i] = ref.arr[i]; return *this; } }; int main() { SimpleArray<int, 5> i5arr1; for(int i = 0; i<5; i++) i5arr1[i] = i*10; SimpleArray<int, 5> i5arr2; i5arr2 = i5arr1; for(int i = 0; i<5; i++) cout<<i5arr2[i]<<", "; cout<<endl; SimpleArray<int, 7> i7arr1; for(int i = 0; i<7; i++) i7arr1[i] = i*10; SimpleArray<int, 7> i7arr2; i7arr2 = i7arr1; for(int i = 0; i<7; i++) cout<<i7arr2[i]<<", "; cout<<endl; return 0; }
|
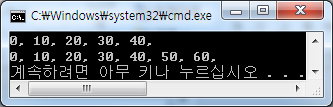
템플릿 매개변수에 디폴트 값 지정
|
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T=int, int len=7> //default value지정 class SimpleArray { private: T arr[len]; public: T& operator[] (int idx) { return arr[idx]; } SimpleArray<T, len>& operator=(const SimpleArray<T, len>&ref) { for(int i=0; i<len; i++) arr[i] = ref.ar[i]; return *this; } }; int main() { SimpleArray<> arr; for(int i=0; i<7; i++) arr[i] = i+1; for(int i=0; i<7; i++) cout<<arr[i]<< " "; cout<<endl; return 0; } |